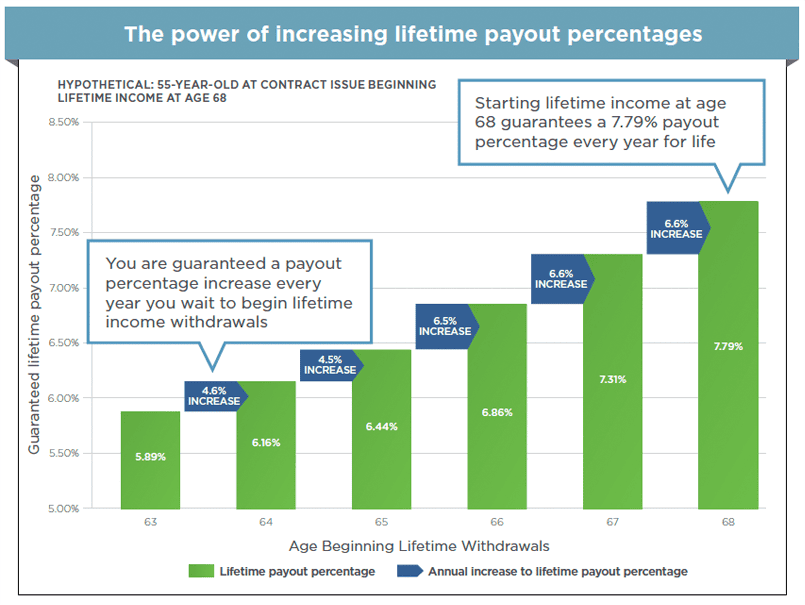
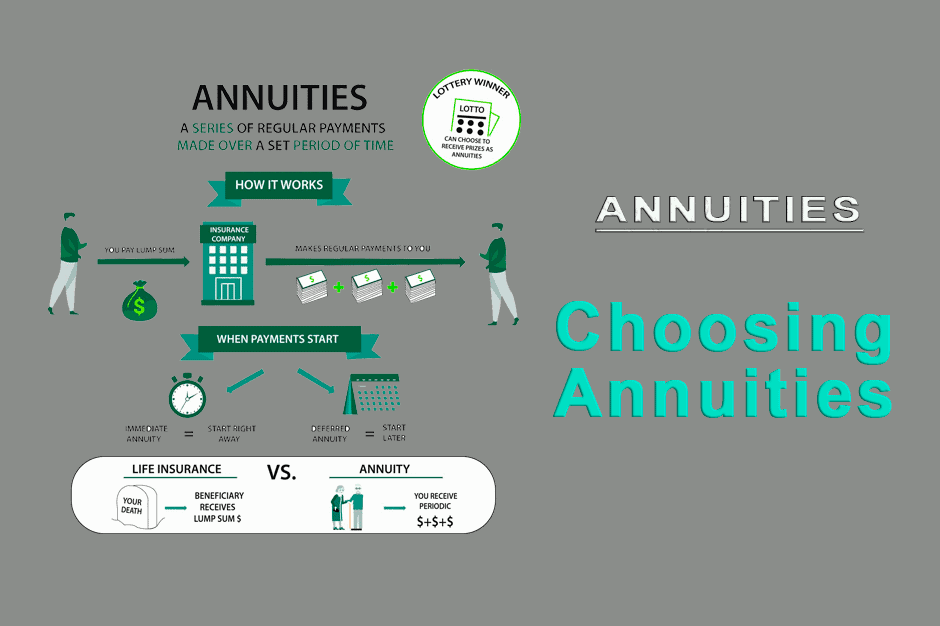
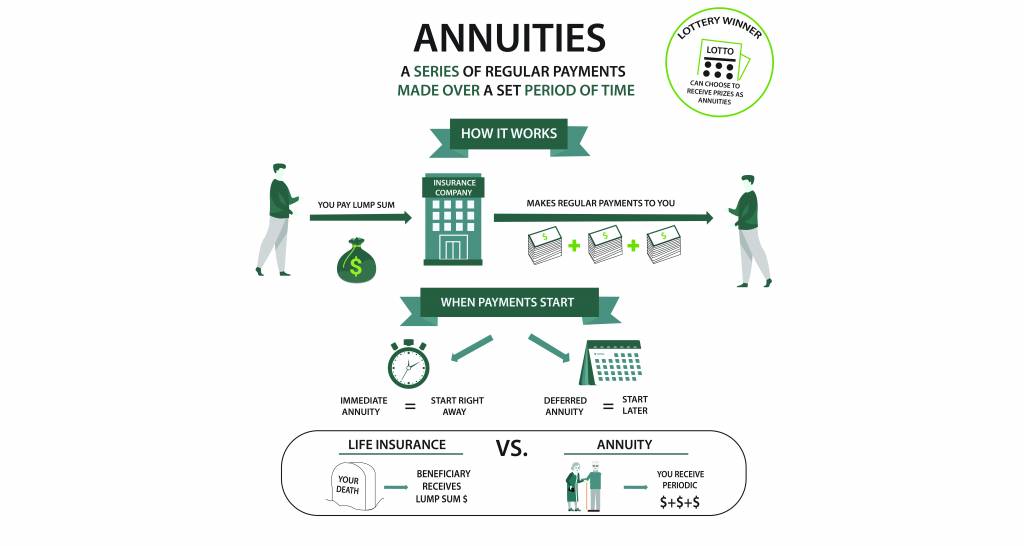
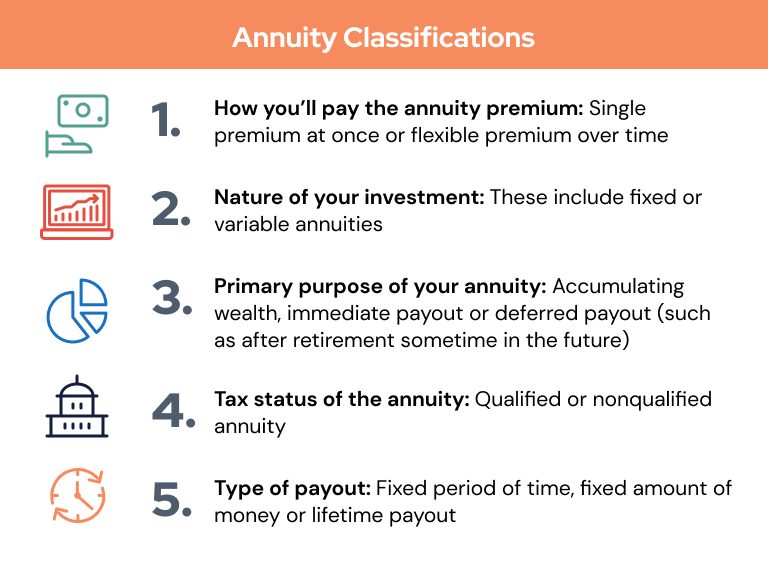
Lifetime Income Annuity: Financial Future with Guaranteed Income. A Lifetime Income Annuity is a financial product designed to provide individuals with a guaranteed income for the rest of their lives. It’s an essential tool for retirement planning, offering a sense of security for those who want to ensure they have a steady cash flow throughout their retirement years. In this article, we will explore what a lifetime income annuity is, how it works, its benefits, types, and considerations to help you make an informed decision.
What is a Lifetime Income Annuity?
A Lifetime grant, also known as a single premium immediate annuity (SPIA), is an insurance contract that promises to pay you a fixed income for the duration of your life, starting immediately after the purchase. You make a lump-sum payment to an insurance company, and in return, they guarantee regular payments to you for as long as you live, regardless of how long you live. This income can act as a safety net, ensuring that you do not outlive your savings.
The amount of the monthly payments depends on various factors, including your age, gender, the amount invested, and the type of annuity you choose. The key advantage of a Lifetime Income Annuity is its ability to provide predictable, reliable income, which can be particularly beneficial during retirement when earning a regular paycheck is no longer an option.
How Does a Lifetime Income Annuity Work?
Once you purchase a Lifetime Income Annuity, you agree to give the insurance company a lump sum payment in exchange for future income. The company then invests the funds and calculates the monthly payment that you will receive. Payments begin right away and continue for the rest of your life.
Here are the steps involved:
- Payment: You pay a lump sum to the insurance company.
- Payout Calculation: The company calculates the amount you will receive based on your life expectancy, investment, and type of annuity.
- Income Payments: The company starts paying you a fixed income that lasts for the rest of your life.
Lifetime Income Annuities can be tailored with additional features, such as inflation protection or a beneficiary option, which allows your beneficiaries to receive a portion of the payments if you pass away prematurely.
Types of Lifetime Income Annuities
There are various types of Lifetime Income Annuities to suit different needs. Understanding the types can help you choose the right product based on your financial goals and preferences:
- Fixed Lifetime Income Annuity:
- Offers a guaranteed, fixed monthly income for life. The amount stays the same throughout the contract period, providing stability.
- Variable Lifetime Income Annuity:
- Payments vary based on the performance of underlying investments. While this offers the potential for higher income, it also comes with more risk.
- Immediate vs. Deferred Annuities:
- An immediate annuity starts payments immediately after purchase, while a deferred annuity delays payments until a future date, often designed for younger individuals planning for retirement.
- Joint Lifetime Income Annuity:
- This option covers two individuals, typically a married couple, ensuring that both receive income for life. Payments continue until both have passed away.
- Lifetime Annuity with Inflation Protection:
- Payments increase over time to keep pace with inflation, ensuring that your purchasing power doesn’t diminish over the years.
- Life Annuity with Period Certain:
- In case of death within a specified period, the annuity continues to be paid to your beneficiaries for that period, ensuring they receive a benefit.
Benefits of a Lifetime Income Annuity
- Guaranteed Lifetime Income:
- The most significant benefit of a Lifetime Income Annuity is the guarantee of income for life, regardless of how long you live. This provides peace of mind and financial security.
- Protection Against Longevity Risk:
- One of the primary concerns during retirement is the risk of outliving your savings. An annuity mitigates this risk by ensuring you will continue to receive income as long as you live.
- Predictable Cash Flow:
- A Lifetime Income grant offers predictable and regular payments, allowing you to plan your budget and manage your finances with confidence.
- No Investment Risk:
- Since payments are fixed, you are not exposed to the risks of market volatility. Unlike other retirement products, such as 401(k)s or IRAs, your income is unaffected by stock market fluctuations.
- Customization:
- Annuities can be tailored to meet your specific needs, including options for beneficiaries, inflation protection, or even adding a guaranteed minimum income benefit.
Considerations Before Purchasing a Lifetime Income Annuity
- Irrevocable Commitment:
- Once you purchase an annuity, the lump sum payment is gone, and you cannot access the principal amount. This means you must be comfortable with the loss of liquidity.
- Inflation Risk:
- Without an inflation rider, the fixed payments may lose purchasing power over time, especially if inflation rises significantly. You may want to consider an annuity with an inflation-adjustment feature.
- Costs and Fees:
- Some annuities come with fees or charges that can reduce the value of your income stream. Be sure to review all associated costs before purchasing.
- No Beneficiary Payouts:
- Unless you opt for additional features like a death benefit, your annuity payments cease upon your death, and no further payments are made to your beneficiaries.
- Life Expectancy Assumptions:
- Annuity providers calculate payouts based on average life expectancy. If you live longer than expected, you benefit; however, if you die earlier than expected, you may not recoup your investment.
10 Tips for Maximizing Your Lifetime Income Annuity
- Consider Your Age: The younger you are, the lower your monthly payout will be, so it’s essential to buy the annuity at an age when it aligns with your retirement planning.
- Evaluate Inflation Protection: Look for annuities that offer inflation-adjusted payouts to maintain your purchasing power over time.
- Understand Fees: Be aware of any hidden fees or administrative charges that could eat into your returns.
- Compare Annuity Providers: Shop around to find the most reputable insurance company offering competitive rates and strong financial stability.
- Understand Your Needs: Choose an annuity that meets your specific retirement goals, whether that’s steady income or flexibility.
- Use a Financial Advisor: Consult a financial advisor to help you make an informed decision that aligns with your long-term goals.
- Consider the Length of Payments: Think about whether you want lifetime payments or a fixed-term payout.
- Diversify Income Sources: A lifetime income grant should complement other retirement assets like 401(k)s and IRAs.
- Know Your Options: Understand all the available options, including joint and survivor annuities or death benefits.
- Be Prepared for the Loss of Liquidity: Once you purchase an annuity, you won’t be able to access the lump sum you invested.
10 Frequently Asked Questions About Lifetime Income Annuities
- What is the difference between a lifetime income annuity and a standard annuity?
- Can I access my money from a lifetime income annuity?
- What happens to my annuity if I pass away?
- Are lifetime income annuities taxable?
- What are the risks associated with a lifetime income annuity?
- How do I calculate the amount I’ll receive from a lifetime income annuity?
- Can I add a beneficiary to my lifetime income annuity?
- Is a lifetime income annuity the same as Social Security?
- How does inflation affect a lifetime income annuity?
- Can I purchase a lifetime income annuity with my 401(k) or IRA?
Conclusion
A Lifetime Income grant offers a secure financial future by providing guaranteed income for life. It helps safeguard against the risk of outliving your savings and provides a steady income stream for retirement. However, like any financial product, it comes with its own set of considerations, such as the loss of liquidity and potential inflation risks. By understanding the types of annuities available, the benefits they offer, and the associated costs, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals and retirement needs.
Ultimately, a Lifetime Income grant can be an excellent tool for achieving financial peace of mind, especially for those looking for stability and predictability in retirement. Always consult with a financial advisor before making any significant investment decisions to ensure you choose the best annuity for your unique situation.