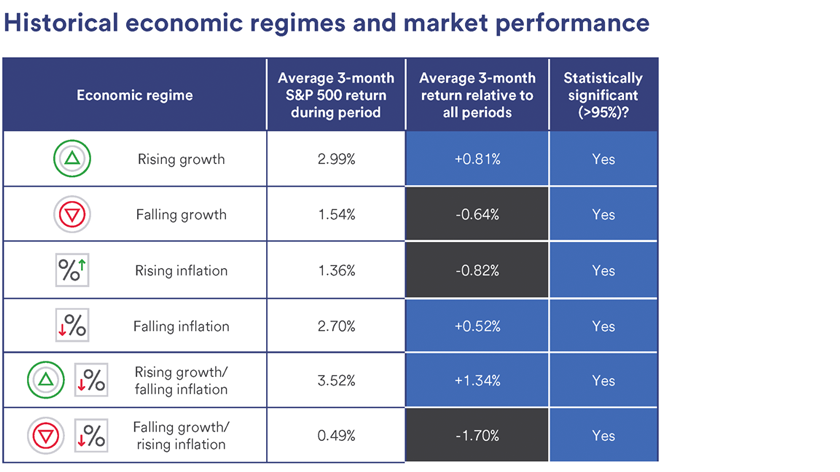
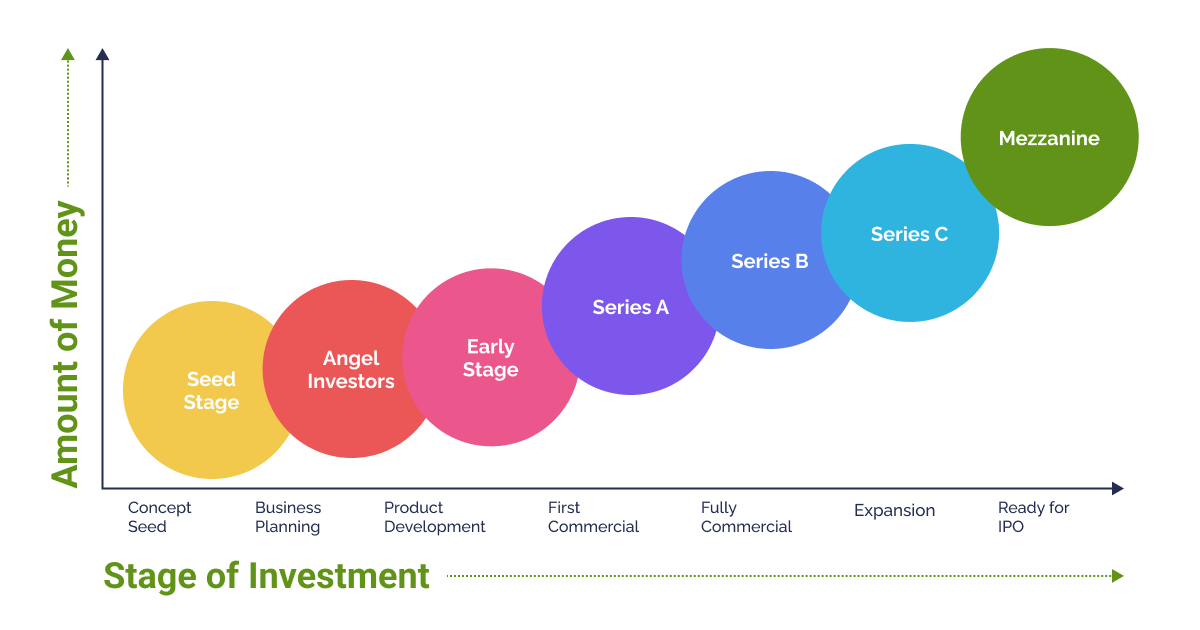
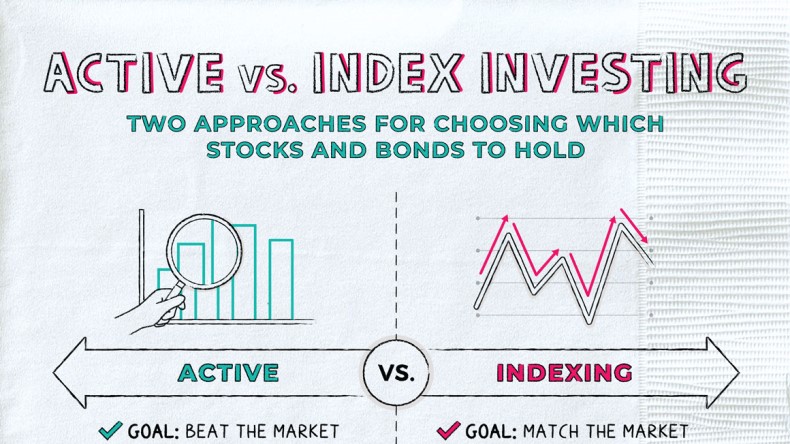
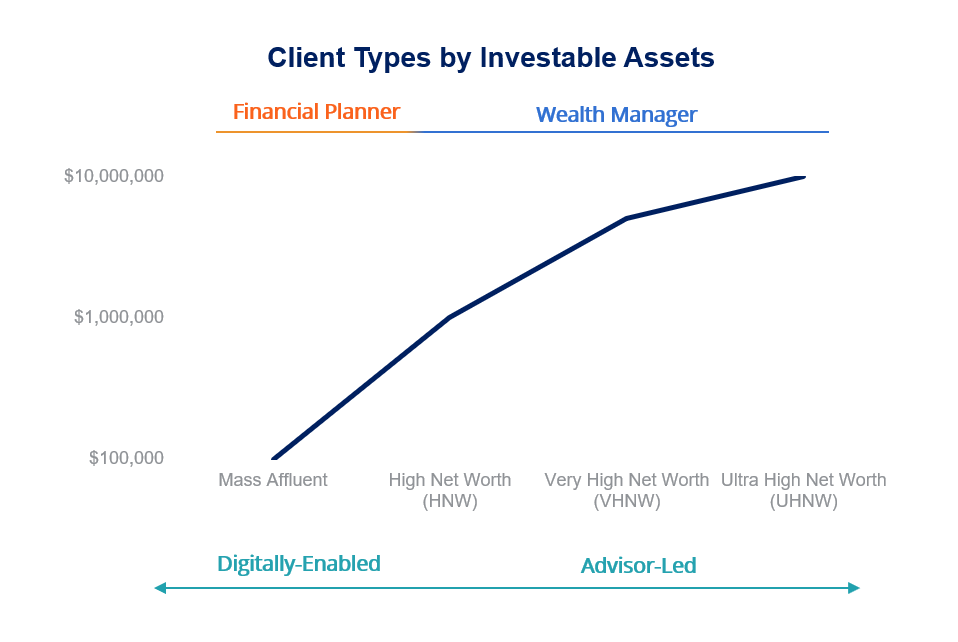
Offshore Investment Accounts: Guide for Smart Investors. Offshore investment accounts are becoming increasingly popular among savvy investors seeking to diversify their portfolios and access international markets. These accounts allow individuals and businesses to invest in foreign assets, often in jurisdictions with favorable tax laws, privacy protections, and financial stability. But while the potential benefits are appealing, offshore investments come with their own set of risks and regulations that must be carefully considered. This article will provide a complete overview of offshore investment accounts, explaining what they are, how they work, and the advantages and disadvantages for both individuals and businesses.
What is an Offshore Investment Account?
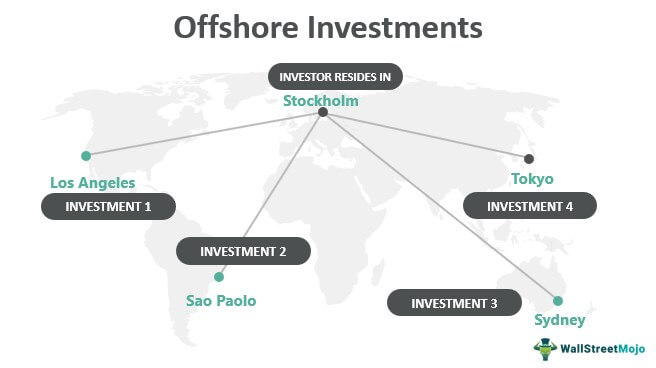
An offshore investment account is a financial account held in a country outside of the investor’s home country. These accounts are typically offered by international banks and financial institutions in jurisdictions known for their favorable tax and regulatory environments. Offshore accounts can be used to invest in a wide range of assets, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, real estate, and other investment vehicles.
The main appeal of offshore accounts is that they provide greater privacy, tax efficiency, and access to global markets. Popular jurisdictions for offshore accounts include the Cayman Islands, Switzerland, Singapore, Luxembourg, and Hong Kong, among others.
How Offshore Investment Accounts Work
Offshore investment accounts function similarly to domestic investment accounts but with certain key differences. The process generally involves selecting a financial institution in a foreign country, opening an account, and then choosing the investment vehicles that suit the investor’s goals. These accounts may require minimum deposits, legal documentation, and compliance with both domestic and international laws.
Some key features of offshore investment accounts include:
- Currency diversification: Offshore accounts allow investors to hold assets in multiple currencies, helping to reduce risk due to currency fluctuations.
- Access to international markets: Offshore accounts can give investors the opportunity to invest in stocks, bonds, and other assets from around the world, providing access to emerging markets and global diversification.
- Tax advantages: Depending on the jurisdiction, offshore accounts may offer tax advantages such as lower capital gains tax rates, tax exemptions on foreign income, and favorable inheritance tax policies.
Advantages of Offshore Investment Accounts
- Tax Efficiency: One of the primary reasons investors choose offshore accounts is for the potential tax benefits. Some jurisdictions offer low or no taxes on income generated from investments, helping to maximize returns. Offshore accounts may also offer exemptions on estate taxes or inheritance taxes, depending on the country.
- Increased Privacy: Offshore accounts are often associated with greater privacy protections. Many offshore jurisdictions have strict confidentiality laws that prevent the disclosure of account information to outside parties, offering greater privacy for investors.
- Global Investment Opportunities: Offshore accounts open up investment opportunities in global markets that may not be available domestically. This allows investors to diversify their portfolios internationally and reduce their exposure to the risks of one particular country or market.
- Asset Protection: Offshore investment accounts can offer a level of asset protection from political or economic instability in the investor’s home country. In some jurisdictions, assets held in offshore accounts may be shielded from legal claims, creditors, or changes in tax laws.
- Currency Diversification: By holding assets in different currencies, investors can reduce the risk of currency depreciation in their home country. This can help preserve wealth over the long term, especially in times of economic uncertainty.
Risks of Offshore Investment Accounts
- Legal and Regulatory Complexities: Offshore investment accounts come with a complicated legal and regulatory landscape. Investors must ensure compliance with both the laws of the country where the account is held and the regulations in their home country. Failure to adhere to these laws can result in penalties, fines, or even criminal charges.
- Cost of Setup and Maintenance: Setting up an offshore account often requires a significant upfront investment, including legal fees, account management fees, and minimum deposit requirements. Additionally, maintaining an offshore account may incur ongoing costs, making it less attractive for smaller investors.
- Currency Risk: While currency diversification can be an advantage, it also introduces the risk of fluctuating exchange rates. Currency depreciation in the country of investment can reduce the value of the account, offsetting any gains made from the investments themselves.
- Lack of Consumer Protections: Offshore financial institutions may not be subject to the same regulatory standards as banks in the investor’s home country. This can result in a lack of consumer protections, making it harder for investors to resolve disputes or recover funds in case of fraud or mismanagement.
- Reputation Risks: Some offshore jurisdictions have been associated with tax avoidance, money laundering, and other illicit activities. As a result, investors who use offshore accounts may face reputational risks, especially if their financial activity is scrutinized by regulatory bodies.
How to Open an Offshore Investment Account
Opening an offshore investment account involves several steps, including selecting a financial institution, submitting necessary documentation, and funding the account. Here’s a brief overview of the process:
- Research and Choose a Jurisdiction: The first step is to choose an offshore jurisdiction that aligns with your investment goals. Some of the most common jurisdictions for offshore investment accounts include Switzerland, the Cayman Islands, and Singapore. Each has its own regulations, tax advantages, and investment opportunities.
- Select a Financial Institution: Once the jurisdiction is chosen, the next step is to select a financial institution that offers offshore investment services. Look for a reputable institution with a strong track record, transparent fee structure, and access to a wide range of investment options.
- Submit Documentation: To open an offshore account, you’ll need to provide personal identification documents, proof of address, and potentially a detailed financial background. This is to comply with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations.
- Fund the Account: Offshore accounts typically require a minimum deposit, which can vary depending on the institution and jurisdiction. Once the account is funded, you can begin making investments.
- Select Investment Vehicles: Offshore investment accounts allow you to invest in a variety of assets, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and real estate. Work with a financial advisor to choose the right investments based on your risk tolerance and financial goals.
10 Tips for Offshore Investment Accounts
- Choose a reputable financial institution with a proven track record.
- Understand the tax implications of offshore accounts in both your home country and the jurisdiction.
- Diversify your portfolio to minimize risks associated with any single investment.
- Work with a financial advisor or tax expert to ensure compliance with international tax laws.
- Be mindful of currency fluctuations when holding assets in foreign currencies.
- Carefully research the political and economic stability of the jurisdiction where you open your account.
- Keep detailed records of your offshore investments to ensure transparency and facilitate tax reporting.
- Stay updated on changes in regulations that could impact your offshore account.
- Consider the long-term benefits and costs associated with maintaining an offshore account.
- Avoid using offshore accounts for illegal activities such as tax evasion or money laundering.
10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is an offshore investment account? An offshore investment account is a financial account held in a foreign country that allows individuals or businesses to invest in a variety of assets, often offering tax advantages and greater privacy.
- Are offshore investment accounts legal? Yes, offshore accounts are legal, but they must comply with both the regulations of the country where the account is held and the home country of the investor.
- How do offshore investment accounts provide tax advantages? Some offshore jurisdictions offer lower taxes on capital gains, foreign income, and inheritance, helping investors maximize their returns.
- Do I need to declare my offshore account to the IRS? Yes, U.S. citizens and residents are required to report offshore accounts to the IRS, typically through the Foreign Bank Account Report (FBAR) and other forms.
- How much do offshore investment accounts cost to maintain? Offshore accounts often come with setup fees, maintenance fees, and minimum deposit requirements. These costs can vary depending on the financial institution and jurisdiction.
- Can I access my offshore account anytime? Yes, offshore accounts generally allow 24/7 access to funds and investments, though some jurisdictions may have restrictions on foreign withdrawals.
- What types of investments can I hold in an offshore account? Offshore accounts allow you to invest in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, real estate, and other financial instruments, depending on the institution.
- How safe are offshore investment accounts? The safety of offshore accounts depends on the jurisdiction and financial institution. It is important to choose a reputable provider with a strong regulatory framework.
- Can I open an offshore account without traveling? Yes, many offshore accounts can be opened remotely, but you will need to provide necessary documentation and meet legal requirements.
- What happens to my offshore account if the bank goes bankrupt? In some jurisdictions, offshore accounts are protected by deposit insurance or similar mechanisms, but this can vary depending on the location and institution.
Conclusion
Offshore investment accounts provide investors with the opportunity to diversify their portfolios, gain access to global markets, and take advantage of favorable tax conditions. However, they also come with certain risks, including legal complexities, costs, and potential reputational concerns. As with any investment, it’s important to conduct thorough research, consult with financial and tax experts, and ensure full compliance with international laws before opening an offshore account.
Ultimately, offshore investment accounts can be a valuable tool for those looking to optimize their investment strategies. By carefully selecting the right jurisdiction, managing risks, and understanding the regulatory environment, investors can leverage the benefits of offshore accounts while mitigating potential drawbacks.