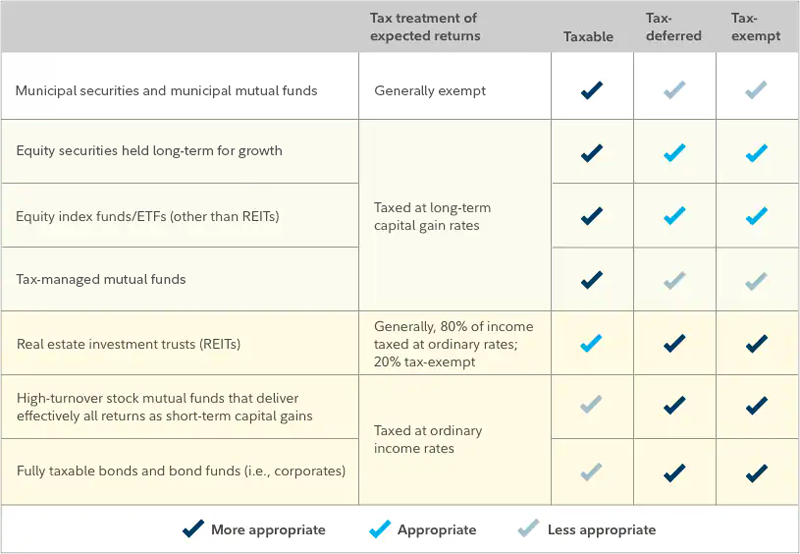
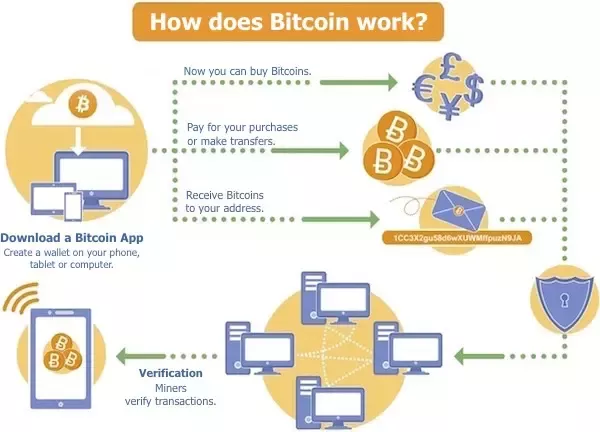
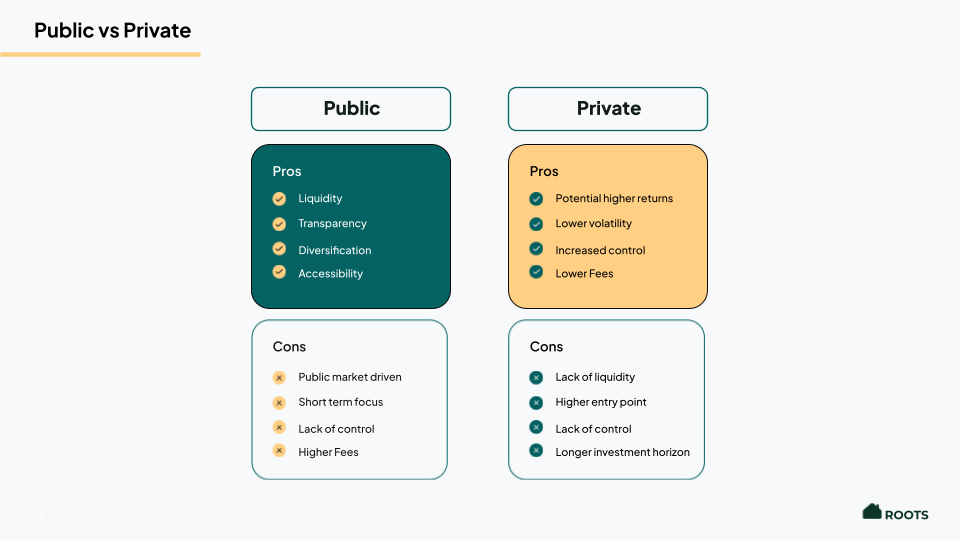
Tax-Advantaged Investment Accounts: Guide to Smart Investing. In today’s financial landscape, understanding the different tax-advantaged investment accounts can significantly improve your ability to grow wealth while minimizing taxes. These accounts offer various benefits, such as tax deductions, tax deferrals, and tax-free earnings, all of which can make a huge difference in long-term wealth accumulation. Whether you’re planning for retirement, education, or just looking to invest smarter, tax-advantaged accounts can be a valuable tool in your investment strategy.
What Are Tax-Advantaged Investment Accounts?
Tax-advantaged investment accounts are specific types of financial accounts designed to help investors reduce the impact of taxes on their investment earnings. These accounts may offer tax deductions on contributions, tax-deferred growth on investments, or tax-free withdrawals, depending on the type of account.
The most common types of tax-advantaged accounts include:
- Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)
- 401(k) Plans
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
- 529 College Savings Plans
- Roth IRAs
Each of these accounts serves different purposes but provides a tax break in some form, which is why they are a popular choice for those looking to optimize their investment strategies.
Why Should You Consider Tax-Advantaged Accounts?
Tax-advantaged accounts are essential for several reasons. Here’s why you should consider using them:
- Tax Savings: The main appeal of these accounts is the tax savings they provide. Whether it’s tax-deferred growth or tax-free withdrawals, these benefits can dramatically boost your investment returns over time.
- Long-Term Growth: Most tax-advantaged accounts allow investments to grow over time without being taxed annually. This means you keep more of your money working for you instead of losing it to taxes.
- Incentive for Retirement Savings: Tax-advantaged retirement accounts like IRAs and 401(k) plans incentivize saving for retirement by offering tax benefits.
- Education Funding: Accounts like 529 Plans are specifically designed to save for education expenses, offering tax-free growth for qualifying educational expenses.
- Health Care Expenses: Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) offer a tax-advantaged way to save for medical expenses, which can help reduce the burden of rising healthcare costs.
Types of Tax-Advantaged Investment Accounts
Here’s a detailed look at the most common tax-advantaged accounts and how they can benefit you:
1. Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)
IRAs are one of the most popular tax-advantaged investment accounts available. There are two main types:
- Traditional IRA: Contributions are typically tax-deductible, and your investments grow tax-deferred until retirement. However, withdrawals are taxed at your regular income tax rate during retirement.
- Roth IRA: Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, but the earnings grow tax-free, and qualified withdrawals are also tax-free. Roth IRAs are particularly advantageous for younger investors who expect to be in a higher tax bracket during retirement.
2. 401(k) Plans
A 401(k) plan is an employer-sponsored retirement savings account. It offers tax-deferral on contributions, meaning you don’t pay taxes on the money you put into the account until you withdraw it. Many employers also offer matching contributions, which can significantly increase your retirement savings.
- Traditional 401(k): Contributions are made pre-tax, and taxes are paid on withdrawals.
- Roth 401(k): Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, but withdrawals are tax-free.
3. Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
HSAs are designed to help individuals save for medical expenses. Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, and the funds grow tax-deferred. When you withdraw the funds for qualifying medical expenses, they are tax-free. An HSA is an excellent tool for individuals with high-deductible health plans (HDHPs).
4. 529 College Savings Plans
529 Plans are state-sponsored accounts designed to help families save for educational expenses. Contributions to these plans grow tax-deferred, and withdrawals used for qualified education expenses are tax-free.
5. Taxable Brokerage Accounts
While not technically tax-advantaged in the same sense as the other accounts, taxable brokerage accounts allow investors to buy and sell stocks, bonds, and other assets. However, any dividends or capital gains are subject to taxation. Still, there are strategies to minimize taxes in these accounts, such as holding investments for over a year to qualify for long-term capital gains rates.
Maximizing Your Investment Strategy with Tax-Advantaged Accounts
To maximize the benefits of tax-advantaged accounts, you need to have a strategy in place. Here are some key tips for making the most of these accounts:
- Start Early: The sooner you begin contributing to tax-advantaged accounts, the more time your investments have to grow tax-free or tax-deferred.
- Take Advantage of Employer Contributions: If your employer offers a 401(k) match, contribute enough to take full advantage of it. This is essentially “free money” for your retirement.
- Diversify Your Accounts: Consider using a combination of IRAs, 401(k)s, and other tax-advantaged accounts to diversify your tax treatment over time. This gives you flexibility in retirement.
- Understand Contribution Limits: Each account has its own contribution limits, so be sure to stay within the limits to avoid penalties.
- Plan for Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs): Traditional IRAs and 401(k)s require RMDs starting at age 73. Make sure you factor this into your retirement planning.
- Use Roth Accounts for Tax-Free Withdrawals: Roth IRAs and Roth 401(k)s can be particularly beneficial if you expect to be in a higher tax bracket during retirement.
- Consider a Taxable Account for Flexibility: While tax-advantaged accounts are ideal for long-term goals, taxable accounts offer more flexibility, especially if you need access to funds before retirement.
- Be Aware of Penalties: Withdrawals from tax-advantaged accounts before reaching retirement age may incur penalties and taxes. Always check the rules before making early withdrawals.
- Monitor Investment Fees: High fees can eat into your returns over time, so be sure to choose low-cost investments within your tax-advantaged accounts.
- Review Your Accounts Regularly: Tax laws and contribution limits change over time, so it’s essential to stay updated and adjust your strategy accordingly.
10 Tips for Using Tax-Advantaged Accounts
- Start contributing as early as possible to maximize tax-free growth.
- Take full advantage of employer 401(k) matching contributions.
- Use Roth IRAs and Roth 401(k)s to benefit from tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
- Contribute up to the maximum allowed to take full advantage of tax benefits.
- Use 529 Plans for education savings to avoid taxes on qualified withdrawals.
- Keep track of your RMDs to avoid penalties in retirement.
- Utilize HSAs for tax-free savings on healthcare expenses.
- Diversify your tax treatment by using a mix of traditional and Roth accounts.
- Monitor your investment fees to ensure you’re getting the most out of your contributions.
- Review your account periodically to ensure it aligns with your changing financial goals.
10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the difference between a Traditional IRA and a Roth IRA?
- A Traditional IRA offers tax-deductible contributions, but withdrawals are taxed. A Roth IRA provides tax-free withdrawals, but contributions are made with after-tax dollars.
- Can I contribute to both a 401(k) and an IRA?
- Yes, you can contribute to both, but your contribution limits will depend on the type of accounts and your income level.
- How much can I contribute to a 529 Plan?
- Contribution limits vary by state, but they are generally quite high, often exceeding $300,000.
- Are there any penalties for withdrawing money from my IRA early?
- Yes, early withdrawals before age 59½ typically incur a 10% penalty, in addition to regular income taxes.
- What’s the benefit of a 401(k) match from my employer?
- Employer matches are essentially free money, helping you grow your retirement savings faster.
- Can I use my HSA for non-medical expenses?
- Yes, but non-medical withdrawals are subject to taxes and penalties.
- What is the maximum contribution for an IRA?
- The maximum contribution for an IRA in 2024 is $6,500 ($7,500 if you’re 50 or older).
- What happens if I don’t take my required minimum distributions?
- If you fail to take your RMD, you may face a penalty of 50% of the amount that should have been withdrawn.
- Can I contribute to a 401(k) if I’m self-employed?
- Yes, self-employed individuals can contribute to a Solo 401(k).
- Are 529 Plans only for college savings?
- No, 529 Plans can also be used for K-12 tuition, in addition to college expenses.
Conclusion
Tax-advantaged investment accounts play a crucial role in helping investors grow their wealth while minimizing tax burdens. Whether you are saving for retirement, education, or healthcare, these accounts offer unique benefits that can support your financial goals. It’s essential to understand the various options available and strategically choose the right accounts to maximize their potential.
By starting early, taking advantage of employer contributions, and diversifying your accounts, you can set yourself up for a more financially secure future. With the right knowledge and planning, tax-advantaged investment accounts can be powerful tools in your overall financial strategy.