Global Stock Markets: Trends and Investment Strategies for 2024. The global stock markets are constantly evolving, influenced by a wide range of economic, political, and technological factors. Understanding the dynamics of these markets is crucial for investors, policymakers, and analysts who seek to navigate the complexities of global finance. In this article, we will explore the current trends in global stock markets, their historical context, key players, and provide actionable insights for both novice and experienced investors.
1. Introduction to Global Stock Markets
Global stock markets refer to the networks of exchanges and financial markets where stocks (also known as equities) are bought and sold. These markets are essential for the global economy, providing companies with access to capital while offering investors opportunities to participate in the economic growth of companies worldwide. The two primary types of stock markets are domestic and international. Domestic markets are those that exist within a single country, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) in the U.S. or the London Stock Exchange (LSE) in the UK, while international markets allow investors to trade across borders, accessing opportunities in emerging markets and developed economies alike.
2. Key Factors Influencing Global Stock Markets
Several factors influence the global stock markets, and understanding them can help investors make informed decisions. Some of the major factors include:
- Economic Indicators: GDP growth, unemployment rates, inflation, and consumer confidence significantly affect market sentiment. Strong economic performance generally leads to positive stock market outcomes.
- Interest Rates: Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve, set interest rates to control inflation and stimulate economic growth. Low-interest rates often encourage borrowing and investment, which can drive stock prices up.
- Political Events: Elections, changes in government policy, and geopolitical tensions (e.g., trade wars) can create volatility in the stock market.
- Technological Innovations: Breakthroughs in technology, particularly in industries like AI, biotech, and green energy, have the potential to transform entire sectors and influence stock prices.
3. Major Global Stock Exchanges and Their Roles
Global stock exchanges are where securities, commodities, and other assets are traded. The most prominent exchanges include:
- New York Stock Exchange (NYSE): Located in the U.S., the NYSE is one of the largest and most well-known exchanges in the world, with many multinational companies listed.
- NASDAQ: Known for its heavy concentration of tech stocks, NASDAQ is another major U.S.-based exchange that plays a key role in global stock trading.
- London Stock Exchange (LSE): One of Europe’s largest exchanges, the LSE is crucial for international trading, particularly in European and emerging market stocks.
- Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE): The TSE is one of the largest exchanges in Asia and is vital for trading Japanese stocks, especially in the technology and automotive sectors.
4. Impact of Global Economic Conditions on Stock Markets
The performance of the global stock markets is closely tied to the overall health of the global economy. Economic slowdowns, recessions, or periods of stagnation can lead to market downturns. Conversely, periods of economic expansion tend to drive stock prices higher as businesses grow and investor confidence increases.
- Recessions: During global recessions, stock markets generally experience declines. However, some sectors, like defensive stocks (e.g., utilities and consumer staples), may perform better during economic downturns.
- Boom Periods: During economic booms, stock markets typically see robust growth as consumer spending increases, businesses expand, and overall investor sentiment improves.
5. Trends in Global Stock Markets for 2024
In 2024, several key trends are shaping the global stock markets, including:
- Tech Industry Growth: Continued innovations in artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and cloud computing are driving growth in the tech sector.
- Sustainable Investing: With growing concerns over climate change, many investors are focusing on environmentally sustainable companies, known as Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) investing.
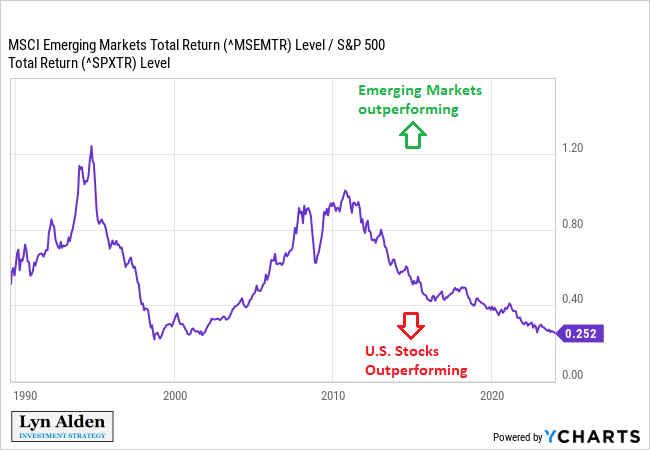
- Emerging Markets: Investors are increasingly looking to emerging markets like India, Brazil, and Africa for growth opportunities, as these regions have the potential for significant economic development.
6. Global Stock Market Volatility and Risk Management
Market volatility is a natural part of the global stock markets. It refers to the fluctuations in stock prices caused by various factors, including economic data releases, political events, and investor sentiment. Managing risk during volatile periods is critical for investors:
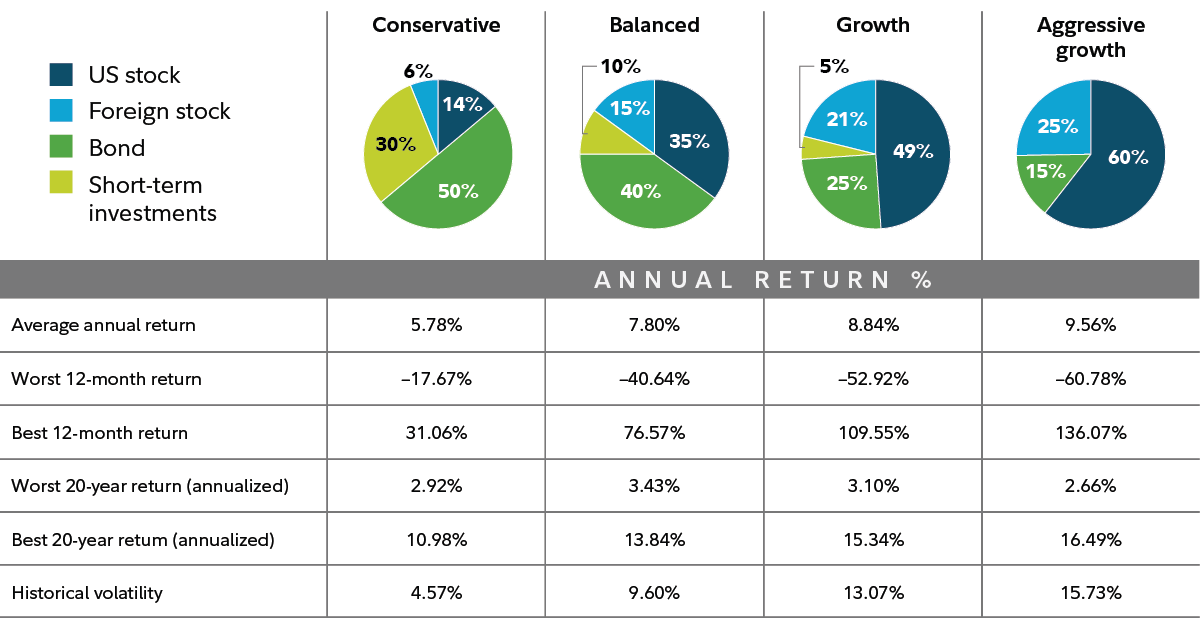
- Diversification: One of the best strategies to manage risk is to diversify investments across multiple asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions.
- Hedging: Investors can use financial instruments such as options or futures contracts to hedge against potential market downturns.
- Long-Term Perspective: Volatility often leads to short-term market declines, but a long-term perspective can help investors ride out fluctuations and benefit from overall market growth.
7. Investment Strategies for Global Stock Markets
There are several strategies that investors can adopt when participating in global stock markets:
- Value Investing: This strategy involves identifying undervalued stocks with solid growth potential, focusing on long-term gains.
- Growth Investing: Investors following this strategy focus on companies with high potential for future growth, even if their stocks appear overpriced.
- Dividend Investing: This strategy involves investing in companies that pay regular dividends, providing a steady income stream for investors.
- Index Funds and ETFs: These funds allow investors to buy a broad range of stocks from different regions and sectors, providing instant diversification.
8. How to Monitor Global Stock Market Performance
Monitoring global stock markets involves staying up-to-date with key indicators such as:
- Stock Market Indices: These include the S&P 500, Dow Jones Industrial Average, FTSE 100, and others that track the performance of a basket of stocks.
- Economic Reports: Data on GDP growth, unemployment, and inflation provide insight into the overall economic health, affecting market performance.
- Corporate Earnings: Quarterly earnings reports from major companies can significantly impact stock prices.
9. The Role of Technology in Shaping Global Stock Markets
Advancements in technology have transformed how global stock markets operate. Algorithmic trading, machine learning, and blockchain technology have all contributed to more efficient and transparent markets. Additionally, online trading platforms have made it easier for retail investors to access global markets and trade stocks in real-time.
10. Future Outlook for Global Stock Markets
Looking ahead, the future of worldwide stock markets appears promising, but it will require investors to stay informed and adaptable to changing conditions. Factors such as rising interest rates, ongoing geopolitical tensions, and the shift towards sustainable investing will continue to shape market dynamics in the years to come.
11. 10 Tips for Investing in Global Stock Markets
- Diversify your portfolio to minimize risk and increase potential returns.
- Keep track of global economic news to stay informed about market trends.
- Invest for the long term to ride out market fluctuations.
- Avoid market timing and focus on a consistent investing strategy.
- Research companies thoroughly before making investment decisions.
- Use index funds or ETFs to get exposure to a wide range of global stocks.
- Consider sustainable investments to align your portfolio with your values.
- Rebalance your portfolio regularly to ensure it aligns with your financial goals.
- Keep an eye on interest rates and their potential impact on stock prices.
- Monitor currency exchange rates when investing in international stocks.
12. 10 FAQs About Global Stock Markets
- What is the global stock market? The global stock market refers to all the markets around the world where securities are traded, including major exchanges like the NYSE, NASDAQ, and LSE.
- How do global economic conditions affect stock prices? Economic indicators like GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment rates directly influence investor confidence and stock prices.
- What are the major global stock exchanges? Some of the biggest exchanges include the NYSE, NASDAQ, LSE, TSE, and others.
- How can I invest in global stock markets? You can invest in worldwide stock markets through individual stocks, ETFs, mutual funds, or index funds that track global markets.
- What is market volatility? Volatility refers to the fluctuations in stock prices caused by various factors, such as economic data, political events, or market sentiment.
- Should I invest in emerging markets? Emerging markets offer potential for high growth, but they come with greater risks. Diversification is key when investing in these markets.
- What is the best strategy for investing in global stock markets? The best strategy depends on your risk tolerance, time horizon, and investment goals. Common strategies include value investing, growth investing, and dividend investing.
- How often should I monitor global stock markets? It’s essential to stay updated on global economic conditions and market trends, but avoid overreacting to short-term fluctuations.
- What is the impact of geopolitical events on stock markets? Geopolitical events such as wars, elections, and trade disputes can create uncertainty and cause market volatility.
- How can I reduce risk when investing in global stocks? Diversifying your portfolio, investing in index funds, and maintaining a long-term investment horizon can help manage risk.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the worldwide stock markets present both opportunities and challenges for investors. By understanding the factors that influence stock prices, following key trends, and adopting appropriate investment strategies, individuals can navigate these markets effectively. Diversification, a long-term perspective, and staying informed are essential for achieving success in the ever-evolving global financial landscape. While volatility is inevitable, those who approach global stock market investing with discipline and knowledge are best positioned to benefit from its growth over time.