Annuity Withdrawal Strategy: Optimize Retirement Income Plan. Planning for retirement requires a clear strategy, especially when it comes to managing annuity withdrawals. An effective annuity withdrawal strategy ensures you maximize your income while minimizing taxes and preserving funds for the future. This article provides an in-depth guide on creating a withdrawal strategy, tips for optimization, and answers to common questions retirees face.
What Is an Annuity Withdrawal Strategy?
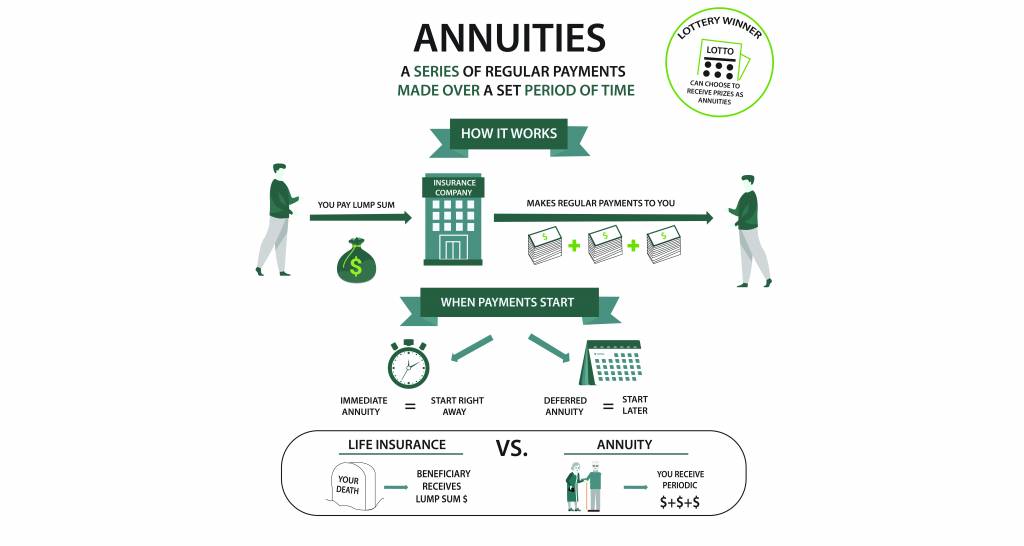
An annuity withdrawal strategy refers to a systematic approach to withdrawing funds from your annuity to meet financial needs during retirement. This strategy balances your cash flow requirements, tax implications, and the longevity of your annuity funds.
Why Is an Effective Strategy Important?
- Ensures Financial Stability: Proper planning helps prevent running out of money in retirement.
- Reduces Tax Liability: Strategic withdrawals can lower the amount of taxes you owe.
- Maximizes Lifetime Income: Stretching your annuity across retirement years provides consistent income.
Factors to Consider When Creating an Annuity Withdrawal Strategy
- Age of Retirement
Early retirement might lead to higher withdrawal rates, risking fund depletion. - Type of Annuity
Fixed, variable, and indexed annuities have different payout structures. - Tax Implications
Withdrawals may be subject to income taxes depending on the annuity type. - Other Income Sources
Consider Social Security, pensions, and savings when planning withdrawals. - Life Expectancy and Health
Estimating longevity ensures you won’t outlive your funds.
Steps to Develop an Optimal Annuity Withdrawal Strategy
- Assess Your Financial Goals
Identify monthly expenses, savings needs, and lifestyle aspirations. - Choose the Right Payout Option
Options include lifetime income, period certain, or lump-sum withdrawals. - Balance Guaranteed and Flexible Income
Combine annuities with other investments for financial flexibility. - Incorporate Inflation Protection
Choose annuities with inflation adjustments to maintain purchasing power. - Work with a Financial Advisor
An expert can tailor strategies to your specific needs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Annuity Withdrawal Strategies
Advantages
- Predictable income during retirement.
- Flexible options for legacy planning.
- Reduces emotional investment decisions.
Disadvantages
- Potential penalties for early withdrawals.
- Limited access to large sums of cash.
- Fees and commissions may reduce returns.
10 Expert Tips for Crafting a Perfect Annuity Withdrawal Strategy
- Start Early: Plan withdrawals during pre-retirement to understand your cash flow needs.
- Diversify Income Streams: Use annuities alongside Social Security and other investments.
- Avoid Early Withdrawals: Penalties can erode your annuity’s value.
- Take Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs): After age 73, ensure compliance with RMD rules.
- Calculate Taxes: Understand the taxable portion of each withdrawal.
- Reassess Regularly: Life changes require periodic strategy reviews.
- Avoid Over-withdrawing: Maintain a sustainable withdrawal rate, typically 4% annually.
- Leverage Immediate Annuities: These provide income right after purchase.
- Account for Health Costs: Budget for unexpected medical expenses.
- Understand Your Contract: Be clear about fees, terms, and payout options.
10 FAQs About Annuity Withdrawal Strategy
- What is the best age to start annuity withdrawals?
Ideally, withdrawals should align with retirement age, often 59½ to avoid penalties. - Are annuity withdrawals taxed?
Yes, taxable portions depend on whether the annuity is qualified or non-qualified. - Can I change my withdrawal strategy?
Some annuities allow adjustments; check your contract terms. - What happens if I outlive my annuity?
Lifetime income annuities ensure payments continue as long as you live. - Are there fees for withdrawals?
Some contracts include surrender charges for early withdrawals. - How does inflation affect my annuity?
Fixed annuities may lose purchasing power, but inflation-adjusted options exist. - What is the difference between qualified and non-qualified annuities?
Qualified annuities are funded with pre-tax money, while non-qualified use after-tax funds. - Can I withdraw a lump sum from my annuity?
Yes, but this can trigger high taxes and penalties. - How do RMDs apply to annuities?
If held in a retirement account, RMD rules apply starting at age 73. - Should I use a financial advisor for my strategy?
Yes, an advisor provides tailored guidance based on your financial goals.
Conclusion
Creating a successful annuity withdrawal strategy is essential for financial security in retirement. A well-thought-out plan maximizes your income, minimizes tax burdens, and provides peace of mind. Consult with a financial professional, regularly assess your needs, and adjust as necessary to ensure long-term stability.
By following the tips and strategies outlined here, you can confidently manage your annuity withdrawals and enjoy a financially secure retirement.